- Domain Relational Calculus uses domain variables that take on values from an attributes domain, rather than for an entire tuple.
- Formal Definition
- An expression in the domain relational calculus is of the form :
- {<x1, x2, …..., xn> | P(x1, x2, …..., xn)}
- Where
- x1, x2, …..., xn represent domain variables.
- P formula composed of atoms.
- An atom in the domain relational calculus has one of the following forms:
- <x1, x2, …..., xn> ϵ r, where r is a relation on n attributes and x1, x2, …..., xn are domain variables or domain constants.
- X Θ y, where x and y are domain variables and Θ is a comparison operator (<, ≤, >, ≥, = , ≠) Attributes x and y have domains that can be compared by Θ
- x Θ c, where x is a domain variable, Θ is a comparison operator, and c is a constant in the domain of the attribute for which x and a domain variables.
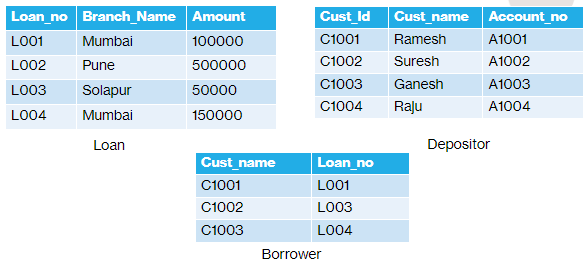
Examples based on following relation.
Answer: => { < l, b, a > | < l, b, a > ϵ loan ᴧ a > 100000 }
Example2: Find the name of all customer who have a loan from the Mumbai branch
Answer: => { < c, a > ∃ l ((<c, l > ϵ borrower ᴧ ∃ b(<l, b, a > ϵ loan ᴧ b = "Mumbai") }